|
|
|
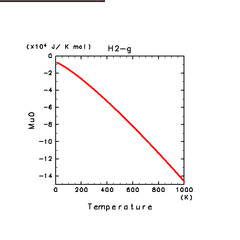
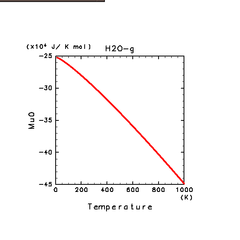
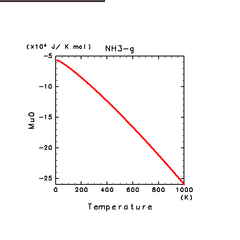
| H2(g) | H2O(g) | NH3(g) |
|
|
|
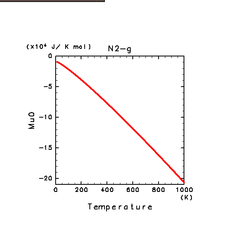
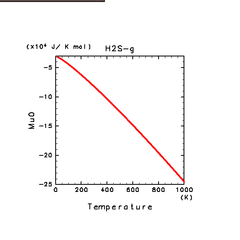
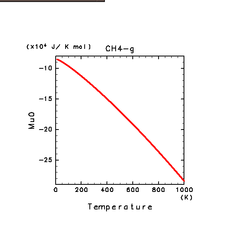
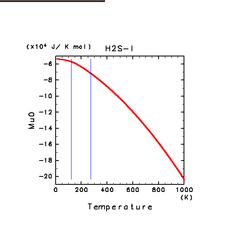
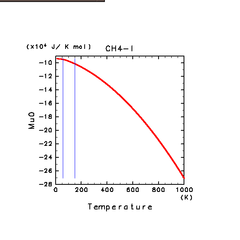
| N2(g) | H2S(g) | CH4(g) |
|
|
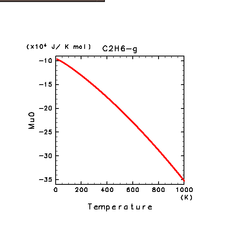
|
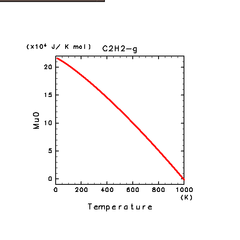
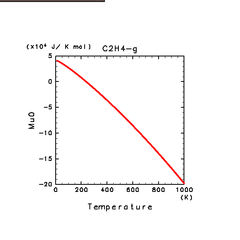
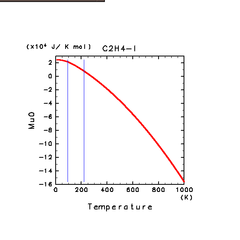
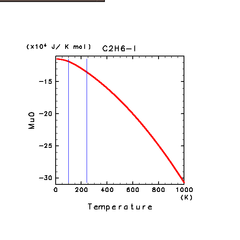
| C2H2(g) | C2H4(g) | C2H6(g) |
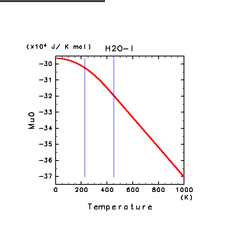
|
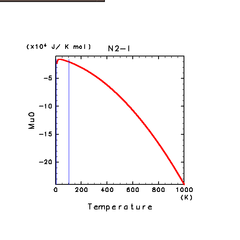
|
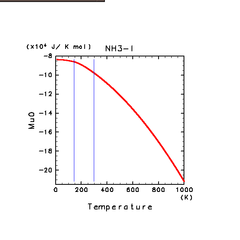
|
| H2O(l) | N2(l) | NH3(l) |
|
|
|
| H2S(l) | CH4(l) | C2H4(l) |
|
|
|
| C2H6(l) | ||
|
|
|
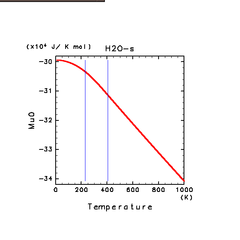
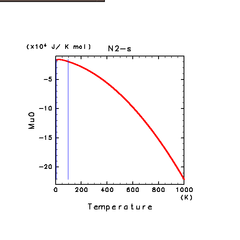
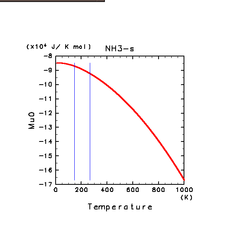
| H2O(s) | N2(s) | NH3(s) |
|
|
|
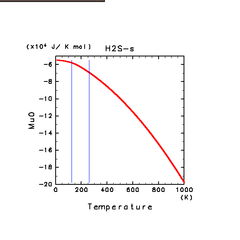
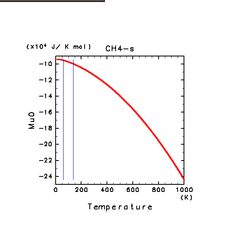
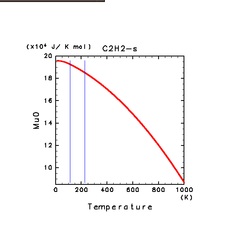
| H2S(s) | CH4(s) | C2H2(s) |
|
|
|
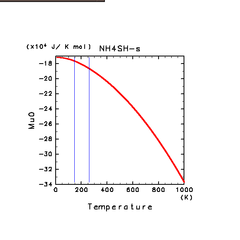
| NH4SH(s) |